TCMEval-SDT: a benchmark dataset for syndrome differentiation thought of traditional Chinese medicine

Background & Summary
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) plays a significant role in the treatment and prevention of diseases and is an important part of the world’s traditional medicine1,2. For example, artemisinin’s effectively treat polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) by mediating the LONP1-CYP11A1 interaction, leading to decreased androgen synthesis3. An herbal-based injection has been demonstrated to be effective in reducing 28-day mortality in patients with sepsis4. Bianzheng Lunzhi (Syndrome Differentiation and Treatment) is a core component of the theoretical framework of TCM. This personalized diagnostic and therapeutic approach involves a comprehensive analysis of various factors, including the patient’s specific disease, constitution, and environmental conditions, to determine the most appropriate treatment plan. Bianzheng Lunzhi represents the fundamental strategy and methodology of clinical practice in TCM5,6.
Over the last few decades, artificial intelligence (AI) has seen rapid advancements in diverse industries. AI is increasingly demonstrating its potential in the medical field, with AI algorithms and models achieving significant results in disease diagnosis, drug discovery, patient car7. To objectively evaluate the performance of these AI algorithms and models, several benchmark datasets are currently being used. For example, DigestPath8 is utilized to assess gastrointestinal pathology detection algorithms, and MultiMedQA serves as the benchmark for evaluating medical questions9.
The diagnostic procedure in TCM clinical practice is different from that of Western medicine in that it diagnoses not only disease but also syndrome. The process of diagnosing a disease contains medical history collection, physical examination, medication use and laboratory tests. However, for diagnosing syndrome, there are no specialized benchmark for the process of syndrome differentiation. Existing benchmark datasets mostly focus on answering basic TCM knowledge questions, such as TCM Bench10, or on evaluating syndromes derived from case analysis, such as TCM-SD11. However, these benchmark datasets do not cover the reasoning process of TCM syndrome diagnosis.
To address the above problems, this study first summarizes the TCM syndrome diagnosis into four steps. (1) clinical information extraction; (2) pathogenesis reasoning; (3) syndrome reasoning; and (4) explanatory summary. Based on this framework, we annotated and curated the TCM medical records. To this end, we have developed TCMEval-SDT, a benchmark dataset specifically designed to evaluate the ability of algorithms or models in TCM clinical diagnosis through syndrome differentiation. Our study aims to advance the development of algorithms or models capable of syndrome differentiation thinking in TCM, such as enabling large language models (LLMs) to think or reason like TCM clinicians during syndrome differentiation using Chain-of-Thought (CoT)12 based on TCMEval-SDT. Ultimately achieve automated diagnosis in the field of TCM. This study has three main objectives:
-
1.
To present a large TCM syndrome diagnosis dataset with the metadata that comply with Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable (FAIR) principles13. For example, medical record ID (DE0087751), clinical Data (DE0087752), clinical information (DE0087755), TCM pathogenesis (DE0087756), TCM syndrome (DE0087757) and explanatory summary (DE0087753).
-
2.
To establish evaluation metrics and allow users to evaluate their answers for performance assessment.
-
3.
To invite users to submit new data to collaboratively build and reuse a benchmark dataset for syndrome diagnosis in TCM, aiming to improve the reusability of data and the overall quality of TCM assessment datasets.
Methods
In this study, the medical records were processed by TCM-Experts, ensuring that all medical records underwent anonymization. A rigorous quality assurance process was implemented to ensure the privacy, accuracy, and reliability of the collected medical records. Subsequently, 300 medical records were selected through manual screening. These records were annotated using Baibu Knowledge Engine14,15, a corpus Tool in the field of TCM that supports automatic annotation, human-machine combined annotation, and manual annotation modes for entity and relation annotation, to construct a comprehensive and systematically organised dataset for TCM syndrome diagnosis.
Data collection
The medical records were sourced from a self-built database established by our team, curated by experts from the Institute of Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine-China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, the Institute of Basic Theory for Chinese Medicine-China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, and senior TCM students. The data were collected from diverse sources, such as the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI, https://www.cnki.net), Wanfang data (https://www.wanfangdata.com.cn), classical Chinese medical texts and medical records from hospitals.
The data were first screened by TCM experts according to the following standards: (1) Complete medical record, including information such as clinical data and clinical experience, etc.; (2) Cases of common diseases. Cases of rare diseases and duplicate cases were excluded. To evaluate the quality of TCM medical records, we developed a TCM Medical Record Quality Assessment Scale (as shown in Table 1) based on the CARE guidelines and TCM expert opinions. This scale comprises ten sub-items, including patient information, clinical findings, timeline, and diagnostic evaluation, to systematically assess the quality of TCM case data. Evaluation results are categorized as “clearly described” “not clearly described” and “ not described” with corresponding scores of 1, 0.5, and 0, respectively16,17. The TCM expert group assessed the quality of the manually screened cases using this scale, excluding cases with scores lower than 6 and including those with scores of 6 or higher.
Data pre-processing and anonymization
The preprocessing workflow for the medical records is shown in Fig. 1. The first step involves anonymizing each medical record by permanently removing identifiable information, such as patient ID and name, to protect patient privacy. The second step entails cleaning and organizing the data by removing duplicate or null data and standardizing the medical records. The FAIR principles serve as foundational guidelines for data sharing and reuse. To support these goals, we designed metadata for medical records in our study that comply with the FAIR principles. We shared the metadata of the TCMEval-SDT dataset on the CDE Portal (https://cdeportal.bmicc.cn), a public metadata registration and management platform, to facilitate the design and management of metadata for similar future projects (as shown in Table 2). We organized unstructured data, including TXT, PDF, Word, and HTML files, into structured data according to metadata requirements, and then assigned a unique identifier to each medical record. Finally, we constructed a benchmark database for syndrome diagnosis, named TCMEval-SDT.
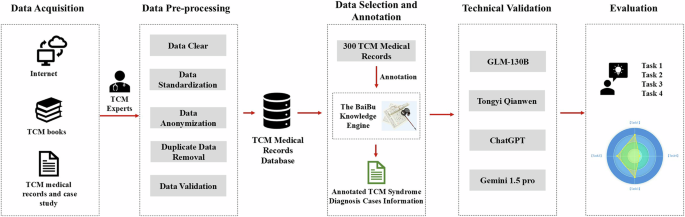
Overview of the data processing workflow and evaluation for the TCMEval-SDT benchmark dataset. The TCM syndrome diagnosis cases sourced from the internet, classical Chinese medical texts, and hospital medical records. The original medical records underwent data preprocessing, including data cleaning, anonymization, and the removal of duplicates, before being stored in a database. From this database, 300 cases meeting specific criteria, such as non-rare cases, were selected. These cases were then annotated and curated by TCM experts using the Baibu knowledge engine. Finally, validation was performed using publicly available LLMs, including GLM-130B, Tongyi Qianwen, ChatGPT, and Gemini 1.5 Pro. Note. TCM = traditional Chinese medical; LLMs = large language models.
Data selection and annotation
The diagnosis of syndromes in TCM is inherently multidimensional, involving a comprehensive evaluation of the interactions between a patient’s physiological, pathological, and environmental factors. For theoretical analysis and practical guidance, we have summarized the TCM syndrome diagnosis process into four steps, as illustrated in Fig. 2.
-
(1)
Clinical Information Extraction: emulating TCM clinicians in obtaining clinical information from the patient’s medical data.
-
(2)
Pathogenesis Reasoning: Inferring TCM pathogenesis from relevant clinical information.
-
(3)
Syndrome Reasoning: Inferring TCM syndromes from relevant TCM pathogenesis.
-
(4)
Explanatory Summary: Summarizing clinical experiences and insights from TCM clinicians.
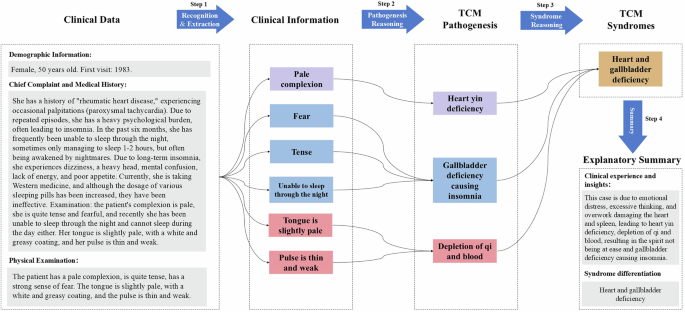
Key steps for syndrome diagnosis of TCM. The figure illustrates the four key steps in TCM syndrome diagnosis. On the left side, the processed clinical data is shown, including the patient’s demographic information, chief complaint, medical history, and physical examination. First step, through recognition and extraction, the patient’s clinical information is obtained. Based on this clinical information, the corresponding TCM pathogenesis is inferred. Then, the TCM pathogenesis is used to inferred the relevant TCM syndromes. Finally, an explanatory summary is provided, emulating the process TCM clinicians follow for syndrome diagnosis. Note. TCM = traditional Chinese medical.
Entity and relation for medical record
We selected 300 medical records and employed the Baibu Knowledge Engine to annotate them according to the aforementioned steps. The annotated entities and their relations are shown in Tables 3, 4.
Annotation guidelines
-
(1)
We classified the clinical information into two types: relevant information and irrelevant information. Relevant information refers to critical clinical information that significantly influences the diagnostic process, while irrelevant information refers to clinical information that does not impact the diagnosis. The annotated entities include only the relevant information in the TCM syndrome diagnosis process. For example, belching (clinical information) – stomach qi upward (TCM pathogenesis) – liver and stomach disharmony (syndrome). Irrelevant information, such as “red tongue with white coating” is excluded from the annotation scope as it does not directly influence this diagnostic process.
-
(2)
It is essential that the annotated entities must be as comprehensive as possible. For example, in “painful distension behind the sternum and in the epigastric region”, the entire phrase must be annotated to prevent loss of critical information by annotating only “painful”.
-
(3)
Inferential relationships exist between clinical information and TCM pathogenesis, and also between TCM pathogenesis and TCM syndromes. For example, extracting clinical information such as “belching” and “depressed state” leads to the inference of TCM pathogenesis, including “stomach qi upward” and “liver-qi stagnation”. Integrating these pathogenic indicators results in the identification of TCM syndromes like “liver and stomach disharmony”.
-
(4)
In this study, the annotation task adheres to a specific rule for long mentions where multiple entities are connected: each entity with independent significance is annotated separately. For example, in the phrase “painful distension behind the sternum and in the epigastric region, burning sensation behind the sternum, sensation of obstruction when swallowing, accompanied by belching and nausea”, the annotation was conducted as follows: “painful distension behind the sternum and in the epigastric region”, “burning sensation behind the sternum”, “sensation of obstruction when swallowing” accompanied by “belching” and “nausea”. This approach ensures that each meaningful entity is properly annotated based on its individual significance.
Example of clinical records annotation through the Baibu Knowledge Engine
Figure 3 illustrates an example of a TCM record annotated using the Baibu Knowledge Engine. TCM experts annotate the clinical Information, TCM pathogenesis, TCM syndrome, and its relations.
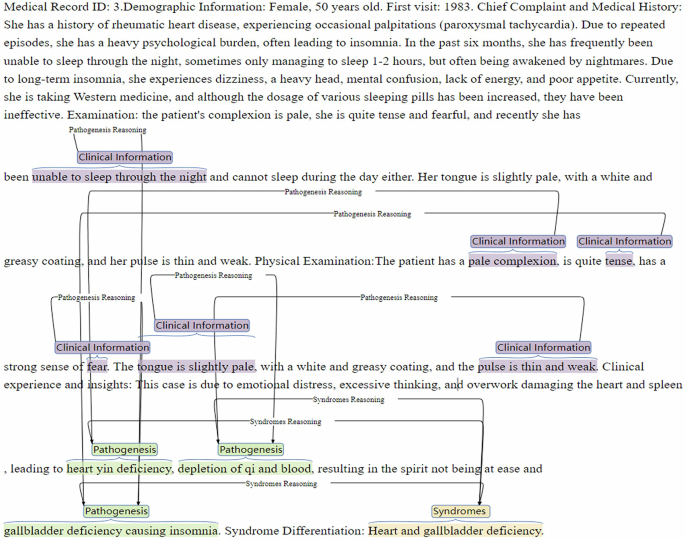
Example of annotation for TCM clinical records. Note. TCM = traditional Chinese medical.
Example of the thought process design in syndrome differentiation
Figure 4 illustrates the detailed design of the thought process in syndrome differentiation. TCM experts extract clinical information and infer TCM pathogenesis based on the clinical data. The inferred pathogenesis is then used to deduce the corresponding syndromes. This process emulates the specific reasoning steps employed by TCM clinicians during syndrome differentiation, providing AI algorithms and models with detailed steps to emulate this reasoning process.
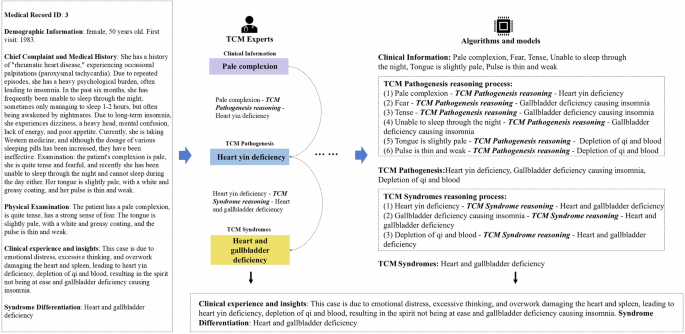
Example of the thought process design in syndrome differentiation. The left side of the figure shows the patient’s clinical data. Based on this data, TCM experts annotate and provide specific guided reasoning steps for the algorithms or models on the right side. Algorithms or models can follow these steps in a step-by-step reasoning process, thereby emulating the detailed procedure by TCM clinicians in syndrome diagnosis. Note. TCM = traditional Chinese medical.
Data evaluation
After the data annotation process was completed, a quality assessment was performed on the 300 medical records used in this study. Each medical record was thoroughly annotated to ensure the completeness and accuracy of the case information. Additionally, to reduce potential biases introduced by incomplete information, all data records were required to contain no missing values. Finally, to maintain the representativeness of the sample, rare medical records were excluded. The final statistics of all TCM medical records, classified according to the ICD-11 for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics (https://icd.who.int/en) are shown in Table 5. All 300 annotated medical records satisfied the aforementioned selection criteria.
Data Records
TCMEval-SDT benchmark dataset is available for access and download on Figshare18, provided under the CC-BY 4.0 license. A total of 300 medical records were incorporated into TCMEval-SDT to create this benchmark dataset. The data were divided into training (n = 200), testing (n = 50), and validation sets (n = 50) following a 4:1:1 ratio. To aid the algorithm or model in performing diagnosis, four subtasks were designed for each case: (1) data extraction; (2) pathogenesis reasoning; (3) syndrome reasoning; and (4) explanation summary. Pathogenesis reasoning and syndrome reasoning were formatted as multiple-choice questions with ten options to assess the model’s diagnostic reasoning ability. The multiple-choice questions on pathogenesis and syndrome reasoning are generated by a Python script (generate_multiple_choice_options.py), which is available on Figshare18. This script first collects the annotated pathogenesis and syndrome data from the TCMEval-SDT dataset, randomizes the options, and creates option lists for pathogenesis and syndrome. Finally, the script generates the ten options multiple-choice questions by selecting the correct options based on medical records, along with randomly selected options from the pathogenesis and syndrome lists. The Python script (evaluate.py) used for technical validation is also available on Figshare18.
The TCMEval-SDT dataset includes three JSON files: (1) Train_TCM_Data_v1.json containing 200 cases, (2) Test_TCM_Data_v1.json containing 50 cases, and (3) Validation_TCM_Data_v1.json containing 50 cases. Table 6 provides an overview of the metadata for the dataset. In TCMTval-SDT, we have designed metadata in accordance with the FAIR principles. All information can be accessed via the CDE Portal, laying the foundation for scientific data sharing in the field of TCM, and supporting more researchers in using and developing TCMTval-SDT. It is important to note that the Test_TCM_Data_v1.json file and Validation_TCM_Data_v1.json file do not include the information of pathogenesis reasoning, syndrome reasoning and its correct answer options.
Technical Validation
In this chapter, we first introduce the criteria for evaluating answers. To validate and evaluate TCMEval-SDT, we selected four publicly available LLMs and randomly selected 50 medical records from the training set (n = 200). Using these records, we constructed zero-shot prompts to compare the TCM syndrome diagnosis capabilities of different LLMs.
Answer evaluation scheme
For the responses generated by LLMs, we have developed evaluation criteria tailored to each of the four tasks.
Task 1 Clinical information extraction:
where Sc is the score of Task 1; |A| is the number of clinical information for medical record extracted by TCM Expert; (|{A}cap {B}|) is the number of intersections of clinical information for medical record extracted by TCM Expert and clinical information for medical record extracted by the LLMs
Task 2 Pathogenesis reasoning:
where Sp is the score of Task 2; A is the set of correct answers of TCM pathogenesis; B is the set of answers selected of TCM pathogenesis by LLMs; (left|Acap Bright|) is the number of options selected correctly by LLMs; |A| is the number of correct answers of TCM pathogenesis; (left|bar{A}cap Bright|) is the number of options selected incorrectly by LLMs.
Task 3 Syndrome reasoning
where Ss is the score of Task 3; A is the set of correct answers of TCM syndrome; B is the set of answers selected of TCM syndrome by LLMs. (left|Acap Bright|) is the number of options selected correctly by LLMs; |A| is the number of correct answers of TCM syndrome; (left|bar{A}cap Bright|) is the number of options selected incorrectly by LLMs.
Task 4 Explanatory summary:
where Sr is the score of Task 4, calculated based on ROUGE-L19; X is the generated text; Y is the reference text.
Final score Sf for LLMs in TCM syndrome diagnosis task is:
where ({omega }_{1}=0.2,{omega }_{2}=0.3,{omega }_{3}=0.4,and,{omega }_{4}=0.1) are the weights assigned to each task score.
Design of experiment and result analysis
In this study, we selected four publicly available LLMs: ChatGPT20, Gemini 1.5-pro21, ChatGLM-130B22, and Tongyi Qianwen23. For each medical record, we designed zero-shot prompts. The validation process consisted of two steps: (1) testing the selected LLMs via API calls and manual queries; (2) manually organizing the responses from the LLMs. We queried the dataset (n = 50) using both API calls and manual questioning, initially verifying whether the responses from the LLMs adhered to the required format. Subsequently, TCM experts reviewed the responses to identify any null values or formatting inconsistencies.
We employed evaluation scripts to assess the responses generated by the LLMs, as illustrated in Fig. 5. Overall, ChatGLM-130B demonstrated the best performance, achieving the highest total weighted score of 24.7378, followed by Gemini 1.5-pro and ChatGPT with weighted scores of 23.1816 and 21.4753, respectively. ChatGLM-130B performed excellently in Task 1 and Task 2 (see Fig. 5b,c), with weighted scores of 6.2112 and 7.98. For Task 3 (see Fig. 5d) and Task 4, Gemini 1.5-pro demonstrated superior performance, with weighted scores of 9.5067 and 1.4765, and ChatGLM-130B performance was slightly inferior. During the experiments, we observed that ChatGLM-130B and Gemini 1.5-pro demonstrated notable proficiency in TCM diagnostic tasks, achieving commendable scores across all four sub-tasks.
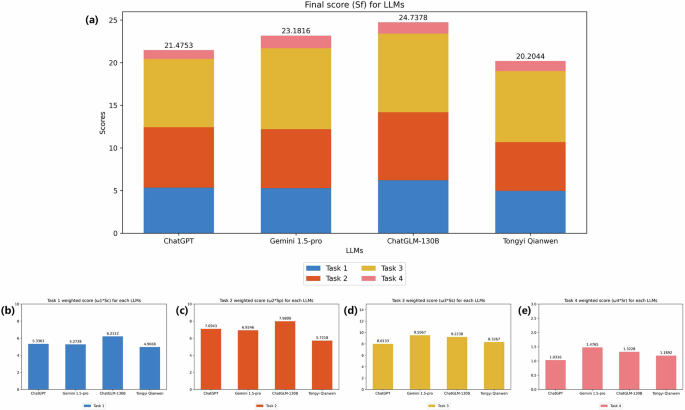
Performance of LLMs on the TCMEval-SDT benchmark dataset(n = 50). Fifty clinical records from the training data were selected for validation, either through API or manual inquiry, and the results were statistically analysed and all scores were calculated based on task weights: ({rm{Task}},1({{rm{omega }}}_{1}=0.2),{rm{Task}},2({{rm{omega }}}_{2}=0.3),{rm{Task}},3({{rm{omega }}}_{3}=0.4),{rm{Task}},4({{rm{omega }}}_{4}=0.1)). The findings indicate that ChatGLM-130B achieved the highest overall performance with a total weighted score of 24.74, excelling in Task 1 and Task 2 with weighted scores of 6.21 and 7.98, respectively. Gemini 1.5 Pro performed best in Task 3 and Task 4, with weighted scores of 9.51 and 1.48, respectively. Note. TCM = traditional Chinese medical; LLMs = large language models.
Usage Notes
The TCMEval-SDT benchmark dataset is available for download and review on Figshare18. This dataset was created to assess the capabilities of algorithms and models in the diagnosis of TCM syndromes. It has been meticulously curated and annotated by TCM experts and includes the following components: Medical Record ID, Medical Data, Explanatory Summary, Syndrome Differentiation, Clinical Information, TCM Pathogenesis, TCM Syndrome, Options of TCM Pathogenesis, Options of TCM Syndrome, Answers of TCM Pathogenesis, and Answers of TCM Syndrome.
However, the released dataset has several limitations. Currently, the dataset is relatively small in size, for example, it contains only four medical record related Qi, blood and fluid disorders,. In the future, we plan to include additional medical records and gradually expand the overall size of the dataset to ensure a more balanced distribution of disease types. Additionally, we aim to incorporate rare disease cases from TCM to develop a more specialized diagnostic dataset. We invite enthusiasts to join our community in enhancing this syndrome diagnosis benchmark dataset and contribute to the advancement of scientific data sharing and reuse.




Responses