Chromosome-level genome assembly of a critically endangered species Leuciscus chuanchicus

Background & Summary
The genus Leuciscus (Cuvier, 1816) is the central group for understanding the phylogeny and systematics of Leuciscinae, and is apparently ancestral for many phylogenetic lineages within the subfamily1,2. More than 40 species are traditionally assigned to this genus, widely distributed throughout Eurasia3. Among them, L. chuanchicus is a medium-sized and omnivorous fish species, feeding mainly on aquatic insects, aquatic plants, and algae. It is an endemic species in the Yellow River, and is distributed only in the upstream of the Yellow River (Fishes of the Yellow river valley). Currently, the population of L. chuanchicus is small, and it is listed on the China Species Red List as a critically endangered (CR) species4. Despite its important status, the genetic and genomic resources for L. chuanchicus are scarce. It is a major challenge for biologists and ecologists to protect endangered species. In the recent era, genomics is becoming an increasingly important approach to conservation biology for understanding genetic diversity in threatened species. The genomic resources can provide detailed information about the present and past demographic parameters, phylogenetic issues, the molecular basis for integrating genetic and environmental methodologies to conservation biology, and for designing fast monitoring tools5,6,7. Unfortunately, due to limited budgets typically for the area of conservation biology, the price for generating a high-quality de novo assembly of most endangered species is still a challenge8. A solution to this problem is enabled by the advancements in long-read genome sequencing technologies combined with the high throughput chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C) technology, which can generate more contiguous assemblies containing scaffolds spanning the length of entire chromosome with inexpensive cost9.
The absence of genomic resources for L. chuanchicus has impeded both phylogenetic studies within Leuciscinae and evidence-based conservation planning. Our study filled this critical knowledge gap by generating the first chromosome-level genome assembly for this critically endangered fish species, and provided a fundamental genomic resources for investigating molecular evolution in Leuciscinae and suggesting genomic-based management strategies.
Methods
Ethics statement
This study was approved by the Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of the Centre for Applied Aquatic Genomics at the Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences. The sample collection process complied with the guidelines of Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences.
Sample collection
An adult L. chuanchicus was collected from Ningxia section of the Yellow River during the Yellow River fisheries resources and environment investigation on 2023. The collection of the sampled fish in this study was permitted by the Bureau of Fisheries and Fishery Administration, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Tissues from the L. chuanchicus were collected and immediately stored in liquid nitrogen until DNA or RNA isolation. High quality DNA was extracted using TIANamp Genomic DNA kit (Tiangen, Beijing, China). Total RNA was extracted using Animal Tissue Total RNA Extraction Kit (Tiangen) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Illumina sequencing and genome survey
Gnomic DNA was isolated from muscle tissues of a single fish. The quality of the DNA was assessed using agarose gel electrophoresis, Nanodrop, and Qubit Fluorometer. High-quality DNA was randomly sheared to 300–500 bp fragments, and a paired-end library was prepared following the manufacturer’s protocol. The library was sequenced on an Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform using a paired-end 150 bp layout to enable genome survey and base-level correction. After removing low-quality, short reads, and adaptor sequences using Fastp v0.23.210, a total of 385,955,792 clean reads were used for the genome survey (Table 1). The K-mer value was set at 19, and K-mer frequencies and K-mer pairs were calculated using KMC v3.2.211. The generated smudgeplot confirmed the proposed diploid of L. chuanchicus (Fig. 1a). Further genome size and heterozygosity ratio was estimated by combining Jellyfish v2.3.012 and GenomeScope v2.013. The survey analysis results showed that the main peak was observed around a depth of 43 (Fig. 1b). The genome size was estimated to be 1.1 Gb, with a heterozygosity rate of 0.53% at K-mer = 19 (Fig. 1b).
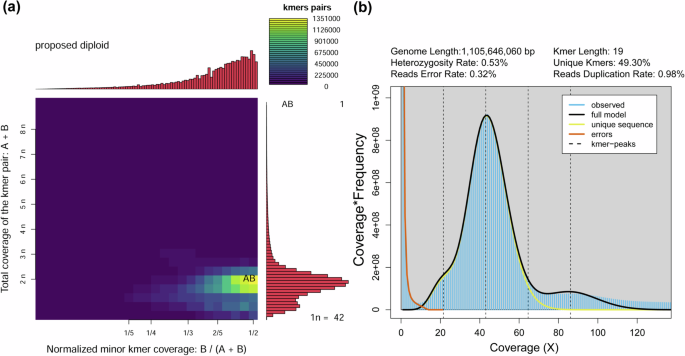
The estimated characteristics of L. chuanchicus genome. (a) Smudgeplot of ploidy estimation. (b) K-mer distribution used to estimate genome size.
PacBio HiFi sequencing and contig-level genome assembly
High-quality genomic DNA was sheared into fragments of approximately 15 Kb in size. After purification and size-selection, the qualified DNA fragments were used for SMRTbell library construction using a SMRTbell Express Template Prep Kit 2.0 (Pacific Biosciences, CA, USA). The library was sequenced on the PacBio Sequel Revio platform utilizing SMRT technology. The PacBio SMRT-Analysis package (https://www.pacb.com) was used for the quality control of the raw polymerase reads. Adaptor sequences, and the polymerase reads with short length or low-quality values were removed. HiFi reads were generated by SMRTLink software with parameters –min-passes = 3 –min-rq = 0.99. After removing low-quality sequences or contaminate sequences, a total of 4,764,355 high-precision long reads with an N50 value of 16,299 bp were obtained (Table 1). Then, the HiFi reads were used for de novo assembly by using Hifiasm v0.16.1 with defaulting parameters14. The resulting draft genome consists of 233 contigs, with a total length of 1,160,128,619 bp and N50 size of 31,116,631 bp (Table 2).
Hi-C sequencing and chromosomal-level genome assembly
To generate a chromosomal-level genome assembly, a Hi-C library was prepared using the genomic DNA isolated from the same L. chuanchicus fish sample, through a series process including crosslinking, cell lysis, chromatin digestion, biotin labelling, proximal chromatin DNA ligation, and DNA purification. The resulting library was sequenced on an Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform. The adaptor sequences, low-quality reads, or reads with 3nt unidentified nucleotides were removed. The filtered Hi-C reads were aligned to the initial draft genome by HiCPro v2.11.415, and only uniquely proper mapped paired-end reads were used for scaffolding by 3D-DNA v18092216. Juicebox v1.11.0817 was then used to order the scaffolds to obtain the final chromosomal-level assembly. The contact map was plotted using HiCExplorer v3.7.218 (Fig. 2). The final genome of L. chuanchicus contained 25 chromosomes, covering 97.84% of the estimated nuclear genome (Table 2). Compared to the genome of L. waleckii19,20, a member of the same genus, the L. chuanchicus genome had a similar genome size, GC contents, and scaffold N50. However, the contig N50, average contig length, and largest contig length of our assembly were much longer, and the scaffold number and gap number was much less than that of L. waleckii (Table 2), indicating the high quality of our assembly of L. chuanchicus genome.
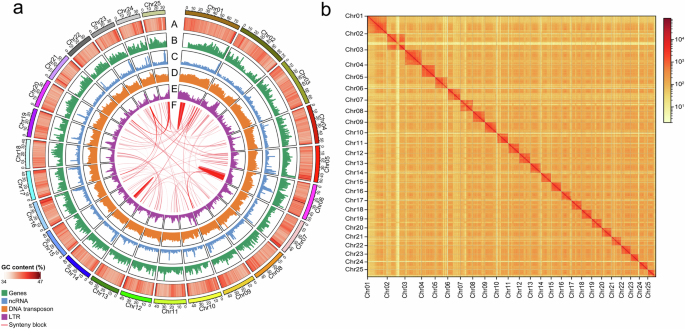
Genomic features and chromosomal interactions in the assembled L. chuanchicus genome showing by circos plot (a) and Hi-C interaction heatmap (b). Tracks in the circos plot from outer to inner layers depict the followings: “A” represents the GC content; “B” represents the gene density; “C” represents the ncRNA density; “D” represents the DNA transposon density; “E” represents the LTR retroelement density; “F” represents the synteny blocks.
Genome annotation
Repetitive elements in the L. chuanchicus genome were identified using a combination of de novo and homology-based methods. The employed tools included MITE-Hunter v1.021, LTRharvest v1.6.222, LTR Finder v1.0723, LTR retriever v2.9.024, RepeatMasker v4.1.125, and RepeatModeler v2.0.2a26. The results showed that the total length of repetitive elements was 667,325,904 bp, accounting for 60.3562% of the assembled genome. Among the repetitive elements, long terminal repeats (LTRs) and DNA transposons were the most abundant, accounting for 24.9193% and 22.5169% of genome, respectively (Table 3).
For protein-coding gene prediction, total RNA was extracted from 9 tissues of L. chuanchicus, including skin, muscle, spleen, intestine, liver, kidney, heart, gill, and brain. Equal amounts of RNA from each tissue were pooled, and used to construct RNA sequencing library. The library was then sequenced on an Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform. A comprehensive strategy combing ab initio prediction, protein-based homology searches, and RNA sequencing was employed to annotate the gene structure. AUGUSTUS v3.5.027, SNAP v6.028, GlimmerHMM v3.0.429 and GeneMark-ET v4.3230 were used to ab initio predict gene structure in the repeat-masked genome. HISAT2 v2.2.131 was used to align the filtered RNA-Seq reads to the genome sequences, and Cufflinks v2.2.132 was used to assemble transcripts GeMoMa v1.933 was then used to perform homology prediction and obtain exon-intron boundary information by comparing the transcript and genome sequences. A total of 31,196 protein-coding genes were successfully predicted in the genome, with an average gene length of 2,467.65 bp, an average CDS length of 1,767.79 bp, and an average exon number of 9.75 (Table 4). Comparing with other ten published fish genome including Tiaroga cobitis34, Rhinichthys klamathensis goyatoka35, Pimephales promelas36, Meda fulgida37, L. waleckii20, Phoxinus phoxinus38, Megalobrama mblycephala39, Ctenopharyngodon idella40, Danio rerio41, and Oryzias latipes42, showed that the number of protein-coding genes, average gene length, average CDS length, average exon length of L. chuanchicus genome were either similar or higher than that of most other fish species, indicating the high quality of the assembled transcriptome annotation. For functional annotation of these predicted genes, all protein-coding genes were aligned to EggNOG, Swiss-Prot, NR, KEGG, and GO database. Of all the predicted genes, 28,323 (90.79%) genes were successfully assigned with at least one functional annotation (Table 5).
For non-coding RNA annotation, tRNAs were identified using tRNAscan-SE43, rRNAs were predicted using RNAmmer44, and ncRNA sequences were searched using INFERNAL v1.1.445. Ultimately, 1,501 miRNA, 17,691 rRNAs, 1,521 snRNAs, and 14,301 rRNAs were identified in the genome, accounted for 0.011547%, 0.180541%, 0.019075%, and 0.091279%, respectively (Table 6).
Data Records
All raw sequencing data including Illumina sequencing data, PacBio HiFi data, Hi-C sequencing data, and transcriptome data have been deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under the accession number SRR2966672946, SRR2966673047, SRR2966672848, and SRR2966672749, respectively. The genome assembly and annotations have been deposited to ENA database under the accession number ERP16907850.
Technical Validation
The quality and completeness of the genome assembly were further evaluated by using BUSCO51 with the actinopterygii_odb10 reference gene set. The final genome assembly showed a BUSCO completeness of 97.6%, consisting of 3,479 (95.6%) single-copy BUSCOs, 72 (2.0%) duplicated BUSCOs, 26 (0.7%) fragmented BUSCOs, and 63 (1.7%) missing BUSCOs (Table 7). The accuracy of the draft assembly was also assessed by mapping Illumina paired-end reads onto the assembled genome sequences. Of total reads, 99.63% were successfully mapped, 93.7% of which were properly paired-end mapped reads, achieving a good genome coverage of 99.97% (Table 8). Further proteome quality assessment was performed using BUSCO and OMArk. The BUSCO assessment showed a completeness of 93% (Table 7), while the OMArk assessment revealed that 91.28% of 16,357 Otophysi hierarchical orthologous groups were complete (Table 9). The high completeness of BUSCOs, high nucleotide-level accuracy, high completeness of OMArks, together with considerable continuity of contig sizes collectively suggest the high quality of genome assembly and annotation of L. chuanchicus produced in this study.



Responses