Developing new varieties of deep-rooted crops: silicon and agroecosystem services

Introduction
Agroecosystems, which cover nearly 40% of Earth’s land surface, are dominant drivers of Earth’s biogeochemical cycling and maintain the vital life-support systems to feed a growing global population via provisioning ecosystem services, such as food and fiber production1. However, agroecosystem sustainable development is under threat due to multiple stresses of environmental and climatic changes such as warming, pest and disease, saline, drought and acidic constraints, and biodiversity loss2,3. Moreover, state-of-the-art climate projections have predicted that the environmental and climatic changes would continuously increase the global intensification of heavy precipitation events and heat extremes and surfaces with stronger or longer-lasting droughts in agroecosystems4,5.
Silicon (Si) is beneficial for crops to maintain a sustainable and smart agroecosystem via alleviating various biotic and abiotic stresses (Fig. 1, Box A). Indeed, Si serves indirectly or directly to crop health, resilience, and food security (Fig. 1, Box A) to benefit humans. Particularly, globally cultivated crops contain 1% or more Si by dry weight, such as rice, wheat, corn, and sugarcane6,7. Despite Si’s critical importance under environmental and climatic stresses, its role in crops remains controversial8. According to the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment9, Si is linked to agroecosystem service10, as it has various beneficial roles immediately and finally serves humans8,11. As illustrated by Fig. 1 (Box A), the Si-related agroecosystem service can be grouped into three categories: (i) supporting services (i.e., primary production, nutrient cycling, soil formation and protection), (ii) provisioning services (i.e., food and energy), and (iii) regulating services (i.e., pest control, crop pollination, climate and flood regulation, and water conservation). Consequently, enhancing plant Si uptake (i.e., silicification degree) improves crop productivity under environmental and climatic stresses8,11. Deep rooting enhances the uptake of soil water and nutrients in the plant12.
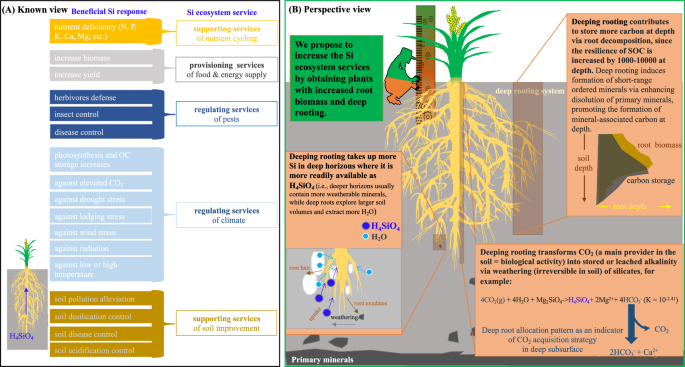
(Box A) Well-known view on conceptualizing key silicon (Si) beneficial responses to the ecology service. This Si ecosystem service supports the service of nutrient cycling and soil improvement, provisioning services for food/energy supply, and regulating pests and climate. (Box B) Perspective view on increasing Si uptake and agroecosystem services by developing new varieties of deep-rooted crops. Facing climate change and land use disturbance in the future, agroecosystems will suffer from several biotic and abiotic stresses, weakening agroecosystem production and its sustainable food system. Sustainable development of agroecosystems is predicted to be exceptionally sensitive to Si uptake. This likely means that enhancing plant Si uptake can improve crop productivity under environmental and climatic change conditions. Deep rooting is an important crop trait that enhances the uptake of soil water and nutrients12. However, little is known about whether and to what extent Si uptake and agroecosystem processes are coupled by developing new varieties of deep-rooted crops. A perspective view on increasing Si uptake and agroecosystem services by obtaining crops with increased root biomass and deep rooting, as it can be involved in several key ecology processes: (i) taking up more Si in deep horizons where it is more readily available as bioavailable silicic acid [i.e., Si(OH)4] (i.e., deeper horizons usually contain more weatherable minerals), which, in turn, gives a beneficial feedback on crop productivity via alleviating drought and environmental stresses; (ii) contributing to store more organic carbon at the depth via root biomass input and the subsequent debris decomposition, and deep pedogenic pathways, since the resilience of soil organic carbon can be increased by 1000–10000 at depth21,36; and (iii) transforming CO2 (main provider in the soil = biological activity) into the stored or leached alkalinity via deep bio-weathering of silicates (irreversible in soil). Responding to these ecosystem processes will require all efforts from plant and soil scientists and agronomists towards better measuring, managing, and utilizing Si cycle and agroecosystem service.
Nevertheless, little is known about whether and to what extent crop silicification can be improved by developing new varieties of deep-rooted crops to link Si agroecosystem services. These knowledge gaps severely limit our understanding and ability to predict the response of agroecosystem biogeochemistry and functions to crop silicification under environmental and climatic changes, lagging the implications of new crop silicification for science, management and governance of agroecosystems. Since the need for increased research attention on Si’s beneficial roles in crops becomes clearer and more urgent13,14, closing these long-neglected knowledge gaps may be a top priority for scientists and decision-makers alike in the sustainable development of agroecosystems.
Here, we discuss whether and to what extent Si-related agroecosystem processes are enhanced by developing new crop varieties with increased root biomass and deep rooting, particularly in the face of intensifying environmental and climatic changes. The agroecosystem processes are involved in (i) taking up more Si in deep horizons where it is more readily available as Si(OH4), responding to crop improvement; (ii) contributing to storing more stable organic carbon at depth via root decomposition and deep pedogenic pathways, and (iii) transforming CO2 into the stored alkalinity or leached alkalinity via boosting primary silicate weathering. These major ecosystem processes are closely involved in vital agroecosystem services: soil and water conservation, climate change mitigation, crop protection and food production. Finally, we propose how to measure or predict agroecosystem services by developing new varieties of deep-rooted crops based on the knowledge of the links between Si mobility and the mentioned agroecosystem processes and services.
Using the genomic approach develops new varieties of deep-rooted crops, likely making it challenging to better optimize deep soil Si mobility process under drought and environmental stresses
In recent decades, considerable progress has been made in plant ecology based on the concept of Si beneficial traits (Fig. 1, Box A). The seminal review by Epstein gives the innovative impulsions of Si in plant science, which has brought about major discoveries in Si uptake in plant tissues and its beneficial effects on plant growth and development8,14,15. However, issues about crop silicification in agricultural ecosystems with intense cultivation should be involved in the ecological significance of deep root Si acquisition on crop yield against environmental and climatic stresses, especially drought and nutrient deficiency. Here, we propose using the genomic approach to develop new crop varieties to favor a steeper, narrower root system by identifying additional candidate genes, challenging the optimization of deep root Si acquisition and agroecosystem processes under environmental and climatic changes. This proposed approach is attributed to manipulating a distribution of deep rooting systems in soils that optimizes water, nutrients and Si uptake, especially under high-density cultivation conditions in intensive smart cropping systems such as rice, wheat, and maize12,16. Drought decreases global crop productivity as it increases in frequency, magnitude, and impact, especially for four main food supplies: rice, wheat, maize, and soybean17,18, due to the limitation of water consumption by agroecosystem19. Silicon benefits wheat’s health, growth, and development under drought stress via leaf phytolith formation (i.e., tissue silicification) in conjunction with plant water loss through transpiration20.
Nevertheless, this coupled mechanism could be considered an approach to developing new varieties with deep-rooted crops to enhance tissue silicification. Deep rooting system allows crops to explore larger soil volumes and extract more Si from less weathered horizons (Fig. 1, Box B), and the increased Si uptake enhances crop tolerance to drought stress and other stresses. Our proposed approach, thus, may open new avenues for plant scientists to make crops more resilient, resource-efficient, and sustainable under drought and nutrient deficiency through a deep root-induced Si biological cycle. The targeted deep-rooted crops can also be closely involved in vital agroecosystem services, such as soil and water conservation and climate change mitigation, as further illustrated by the discussion below.
Deeping rooting affects soil organic carbon dynamics
Understanding the driver of soil organic carbon (SOC) dynamics is a prerequisite to predicting better the net balance of carbon accrual and loss in terrestrial ecosystems. This OC storage in soils has been suggested as a large-scale land-based mitigation possibility21. The SOC is formed via partial decomposition and transformation of above- and below-ground plant debris with microorganisms22. It has been highly recommended as a straightforward management in agroecosystems to maximize root-derived OC input to effectively promote SOC storage at depth, reducing atmospheric CO2, as these increased SOC at deep depth are also characterized by a much longer residence time23. Indeed, both analytical and experimental evidence indicate that the mean residence time of global SOC in the 30–100 cm depth subsoil is approximately four-fold longer than that in the topsoil of 0–30 cm depth24,25. This recommendation might be maximized by targeting new varieties with deep-rooted crops via two potential possibilities. First, deep rooting of new varieties directly enhances the accumulation of living organic matter (i.e., great root biomass) that will be transformed into dead OC in deep soils with depth (Fig. 1, Box B). Second, as discussed above, the deep root-induced Si biological cycle would be involved in enlarging soil volume and facilitating less weathered horizons to release bioavailable Si. This biological process, in turn, promotes both above- and below-ground crop biomass against the potential stresses (Fig. 1, Box B), further responding to the accumulation of SOC in depth. However, soil scientists should further investigate their coupled mechanisms on extending the time that assimilates OC storage.
Deep rooting accelerates deep pedogenic processes to promote soil aggregation and OC stability
Soil aggregation is crucial in maintaining root growth and ecosystem processes and services such as OC storage, resistance to erosion, and surface water and nutrient retention via breeding formation and stabilization of soil structure26. However, aggregation can be largely affected by the traits of fine roots and soil mineral compositions, as well as their interactions27,28. On the one hand, fine roots generally offer a curial OC debris to form extremely stable micro aggregates26,28. Thus, root depth strongly regulates soil structure stability on slopes to reduce runoff, soil erosion, and nutrient leaching28. On the other hand, the stability of soil aggregates partly represents the geochemical factors that regulate the accrual of persistent SOC27. This persistence is attributed to the SOC being physically protected within micro aggregates or co-precipitating with minerals in the form of mineral-associated OC26. Fine roots and their interaction with primary and secondary colloidal particles are also crucial in boosting soil aggregation because they facilitate the encounter of soil mineral particles and bring soil material together29. Indeed, fine root growth at depth affects soil porosity and water infiltration, notably promoting the neoformation of short-range ordered mineral substances and the release of dissolved Si, Al, and Fe via enhancing the weathering of primary minerals29,30. Thus, their interaction with the deep rooting would likely enhance OC stabilization, contributing to achieving the objective of ‘4 per mille Soils for Food Security and Climate’25. This objective could be attributed to the deep pedogenic processes involved in the positive feedback from a deep rooting via the neoformation of short-range ordered minerals such as ferrihydrite and allophanic substances. This happens especially in the topsoil29, where this feedback integrates the source of fine roots at deep depth, therefore coupling to build the enhanced soil aggregation. This further links deep root traits and the structure of soil C sequestration (Fig. 1, Box B), deep soil water retention and Si mobility. This relative ecological process can also be considered deep soil conservation by agronomists to reduce soil erosion and conserve water resources by optimizing agroecosystem management practices.
Deep silicate weathering transforms atmospheric CO2 into the stored alkalinity or leached alkalinity
When deep rooting approaches the weatherable bedrock, fine roots in deep soils slowly dissolve some weatherable minerals to react with atmospheric CO2 of soil pores to form the carbonates (Fig. 1, Box B). This deep root-induced bio-weathering is early involved in the fine roots with high surface area to secrete organic acids and chelates to attack weatherable silicate minerals to acquire the water, nutrients and Si29,31,32, which are coupled with the atmospheric CO2 removal33. A representative weathering reaction of primary mineral (e.g., forsterite) with CO2 is as follows:
In this case, an acceleration of deep rooting-induced bio-weathering by developing new crop varieties should be considered as an approach partly balancing the relationship between climate change and the level of atmospheric CO2 (Fig. 1, Box B). Enhanced rock weathering has been suggested as promising as other strategies for large-scale CO2 removal from the atmosphere because of its relatively low cost and high CO2-removal potential (i.e., using this approach in agroecosystem has been estimated to sequestrate 0.5–2 billion tonnes of atmospheric CO2 each year)34. Furthermore, along with relatively deep rooting, there is additional evidence of a progressive increase in the biological activities of soil depth16, partly enhancing CO2 removal via deep bio-weathering. First, deep-rooting development can induce the abundance of fine root-associated bacteria, whereas the latter generally drives silicate weathering via releasing organic acids35. Second, the decomposition of deep root litter also releases additional acids (e.g., HCO3– and organic acids)29. These two processes likely transform atmospheric CO2 into the stored alkalinity in deep soils (i.e., carbonate minerals). In addition, along with the formation of these stored alkalinities, some leached alkalinity (i.e., CO32- and HCO3–) could be further carried to the ocean by water flow33. Together, quantifying these effects on CO2 balance through observations, measurement, and modelling may enable the prediction of the realized response of deep rooting-induced bio-weathering by developing new crop varieties to climate change. As illustrated by Fig. 1 (Box B), this likely enhances our understanding of deep root allocation pattern as an indicator of CO2 acquisition strategy in deep subsurface with developing new crop varieties.
Concluding remarks and future challenges
Since ecosystem service links ecology and society, it has been a key study issue regarding ecology, natural resource management, and policy implementation. Although this concept is increasingly used in different contexts, a clear definition of ecosystem services provided by deep-rooted crops should be provided to couple the role of Si in agroecosystem. However, applying new concepts may fail due to a lack of a well-focused framework. It needs better integration between ‘root traits’ and ‘crop stress responses’ and a precise focus on the link between crop Si uptake (e.g., tissue silicification) and a key ecosystem process. Thus, we further propose to build up a model of ‘Science and Technology smart agroecosystems’ at a small-scale system, which may be confined in a cropland (i.e., a smallholder farm) that stimulates the ‘Science’ (knowledge to farmers for deep mineral weathering as Si source) with ‘Technology’ (new crop varieties with deep root) to promote new technical strategy and its feedback between root traits (i.e., the uptake of deep water and Si mobility) and Si agroecosystem processes. This may benefit us to measure and compare the practical outcome with an analyzed value coupled with the interaction between deep rooting and the Si biological cycle. For example, when facing drought, we compare the outcome of an agroecosystem productivity model via assessing the Si uptake level (i.e., silicification degree) induced by technical stimulated varieties with deep-rooted crops. Based on the case models using the small-scale agroecosystem, this strategy could be applied to future predictions at a global-scale agroecosystem, strengthening our understanding and ability to forecast the global drought effect. Silicon-based crop production, thus, would open new avenues for plant scientists to increase the root Si acquisition via developing new varieties with deep-rooted crops, maintaining crop yield and food security, and enhancing the Si benefits and agroecosystem service. Focusing research attention on the interaction of new varieties of deep-rooted crops with high levels of soil heterogeneity and Si mobility in agroecosystems will create powerful opportunities for soil and plant scientists against drought and environmental stresses, enhancing the knowledge for agronomists on scientifically optimizing management practices to sustain vital food-support systems.
Responses