Gender disparities in health and wellbeing of older population in India

Ageing, gender and health in India
India currently the most populous country in the world with 1.43 billion people, is experiencing rapid ageing transition. The elderly population of India ages 60 years an above, which numbered 149 million in 2022 (or 10% of the total population), is projected to rise to 347 million (or 20%) in 20501. Women in India with a life expectancy of 73.6 years now live longer than men with a life expectancy of 70.5 years; consequently, older women outnumber older men1. Although women live longer than men, they experience longer period of disease and disability throughout life with older women experiencing higher burden of non-fatal and women specific chronic health condition2,3. Additionally, older women in India with the largest share of widowed women (54% among women aged 60 + ) experience acute economic hardships, social disadvantage and longer period of ill-health and disability4,5. India’s deeply rooted patriarchal structure perpetuates a cycle of female deprivation resulting in gender inequality that spans across generations6,7,8. In addition to significant disadvantage faced by girls from birth thorough adulthood, patriarchal social norms continue to influence various aspects of society, including household family dynamics, institutions, policy-making, and ideological discourses9,10.
Research on women’s health until recently has been largely focused on sexual and reproductive health concerns, which, although are crucial, do not encompass the full spectrum of health issues affecting females throughout their life course11. Evidence-based assessment of gender disparities in disease burden and disability at older ages is necessary to inform gender focussed ageing and healthcare policy initiatives. India’s recent Longitudinal Ageing Study in India (LASI, 2017–18) provide a formidable range of national and statewide database for designing policies and programmes for the older population in the broad domains of social, psychological, health and economic wellbeing12. The Longitudinal Ageing Study in India (LASI) is a comprehensive nationwide survey of 73,250 individuals aged 45 and older, including over 32,000 aged 60 and above representing India and all of its 36 states and Union Territories. LASI is the largest ageing study globally by sample size, sufficiently powered for national and state-level analyses, as well as across socioeconomic spectrum (rural-urban, male-female, and age groups). More detailed information about LASI design, sample size estimation and study protocols are available elsewhere12.
The aim of this commentary is to raise awareness on the critical issue of gender disparities in health and wellbeing of India’s older population using LASI survey data and inform policy decisions focused on older women in India. First, we highlight pronounced gender disparities in health and wellbeing of India’s older population and, how India’s older women are worse off than older men (Fig. 1). Additionally, consistent with the well-documented literature on regional disparities in health indicators10,13, the subnational pattern of gender disparities in health and wellbeing outcomes are reported (Table 1). While population ageing and epidemiological transition is observed across all Indian states and Union Territories, the pace and extent are not uniform reflecting significant subnational variations4,13.
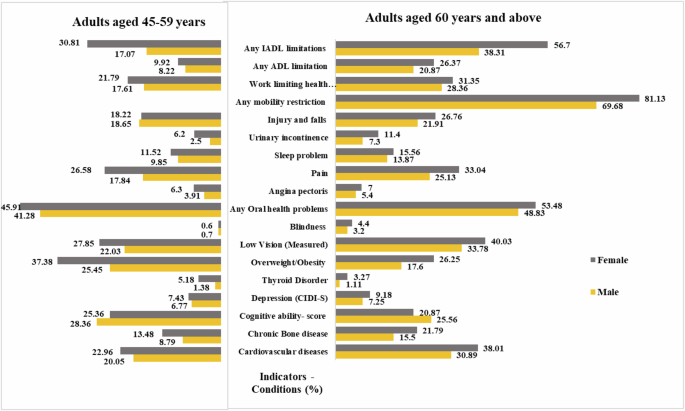
Cardiovascular diseases include hypertension, heart diseases and stroke. Chronic bone diseases include arthritis, rheumatism, and osteoporosis. Any oral health problems include dental caries, periodontal diseases, and common oral health problems. Angina pectoris, pain and sleep problems are symptom-based conditions. Any mobility disorders were only for adults aged 60 + years. All indicators are presented in % except cognition. Cognition – is represented by a composite score generated based on five domains of cognition: memory, orientation, attention, naming, and executive function.
Two theoretical premises provide a potential analytical basis for examining evidence-based gender disparities in health and wellbeing of India’s older population including the empirical connection with India’s patriarchal structure. First, gender analysis frameworks can be applied to document gender disparities in non-communicable diseases (NCDs) and wellbeing outcomes by examining the influence of economic, social and cultural factors on health behaviours14. Second, the construct of Cumulative Disadvantage/Advantage (CAD) theory provides a robust basis how early life-health, and social adversities intensify mid-life health disparities leading to a widening of health and wellbeing disparities at old ages8,15. Together, these factors contribute to higher cumulative burden of disability, health losses and poorer quality of life for older women.
Gender disparities in chronic health conditions and wellbeing measures
Figure 1 shows gender disparities in several critical domains of physical and mental health including chronic health conditions, mental health conditions, metabolic risk factors, symptom-based health conditions, women specific health conditions and functional health measures. In the domain of cardiovascular health, 39% of older women aged 60 years and above reported cardiovascular disease (CVD) which included hypertension, heart disease and stroke, compared to 31% of older men. Similarly, a higher proportion of older women (22%) than older men (16%) reported bone/joint disease. Older women also reported higher prevalence of anaemia and cancer than older men.
In terms of metabolic health, the prevalence of overweight/obesity is more common among older women (26%)) than older men (17%) with high-risk waist circumference more widely prevalent among older adult women (39% for women 9% for men). Thyroid, a metabolic disorder is commonly prevalent among older women. The proportionately higher burden of these metabolic health risk conditions among older women raises their vulnerability to higher burden of non-communicable diseases, disability, and overall poor health. Older women than older men reported much higher prevalence of low vision (40%), hearing impairment, and oral health problems (53%) compromising their overall quality of life and wellbeing. Consequently, a higher proportion of older women than men, and more of those with no schooling, currently not working and widowed reported poor self-rated health4.
Gender differences in mental health components particularly cognitive ability and depression (based on Composite International Diagnostic Instrument – Short Form CIDI-SF scale) are more pronounced16. The prevalence of depression was higher (9.2%) for older women compared to older men (7.2%). Cognitive ability scores also revealed that older women had lower cognitive function scores (20.87) than older men (25.25), likely due to lower literacy and education levels among older women in India4 India has a higher share of widowed women due to both significant marriage age gaps and longer life expectancy of older women. Widowed women are particularly at high risk of depression, cognitive decline, functional limitations and metabolic risk factors. Additionally, discrimination, neglect, abuse, and ill treatment are more common for widowed older women4,17.
A number of elderly women specific acute health conditions are widely prevalent. Uurinary incontinence, a debilitating condition more commonly affecting older women (11%) presents a significant health problem with many older women experiencing more acute and rarer types of urinary incontinence. This condition increases 2-3-fold among those with kidney and bone disease, lung, and cardiovascular diseases, multimorbidity and other acute chronic conditions. Chronic bone disease was more widely prevalent among older women (22%) than older men (16%). Older females typically experience age-related bone loss at a faster rate than males, increasing their risk of osteoporosis18. Also, women aged 45-59 reported significant reproductive health problems including menstrual, menopausal, or gynaecological health concerns.
The data on health symptoms, injuries, endemic diseases, and women health issues revealed older women than men reported higher prevalence of these health condition including angina pectoris, sleep problems, pain and endemic diseases. Almost a third of older women (33%) reported chronic pain compared to a quarter of older men (25%). Similarly, older women reported higher prevalence of injuries and falls (27%) compared to older men (22%). Mobility is one of the important components of functional health and a significant component of self-care and the ability to access essential public services. Eighty one percent of elderly women reported any type of mobility restrictions – walking, climbing stairs, stretching arms etc. Older women also reported higher rate of (32%) of work limiting health conditions. In terms of functional health measure 1 + IADL (Instrumental Activity of Daily Living), almost three fifths of older women (57%) compared to over a third of older men (38%) reported any IADL limitations.
Subnational pattern of gender disparities in health and wellbeing
Table 1 reveals significant gender differences across various health and well-being indicators in most states and union territories of India. Overall, the prevalence rates of cardiovascular disease (CVD), bone diseases, low vision, oral health problems, mobility restrictions, and functional abilities (ADL, IADL) were higher among older women than older men by more than ten percentage points in the majority of the states and union territories.
Among older women aged 60 and above, the prevalence rate of cardiovascular disease (CVD) exceeds 50% in nine of the 36 Indian states, compared to just two states for older men in the same age group. The highest prevalence rates among older women are found in Goa (64%), Chandigarh (63%), Sikkim (61%), Kerala (58%), and Jammu and Kashmir (57%). In contrast, the highest prevalence rates for older men are lower, with Goa at 56%, Kerala at 55%, Sikkim at 54%, Andaman & Nicobar Islands at 50%, and Chandigarh at 48%. Similarly, the highest prevalence of bone disease among older women is observed in West Bengal (37%), Telangana (36%), Kerala (35%), Jammu & Kashmir (33%), and Andaman & Nicobar Islands (31%). For older men, the highest prevalence rates of bone disease are reported in the lower range in the states of Telangana (30%), West Bengal (29%), Maharashtra (22%), Tamil Nadu (22%), and Jammu and Kashmir (22%).
Older women in the northern Indian states of Haryana (14%), Punjab (14%), Himachal Pradesh (10%), Madhya Pradesh (10%), and Uttar Pradesh reported a higher prevalence of thyroid disorders. Additionally, the gender difference in the prevalence of depression was more pronounced in Bihar (7.4% women vs. 5.4% men), Chandigarh (8.6% vs. 5.8%), Goa (10.4% vs. 6.5%), Punjab (9.9% vs. 6.3%), and Uttar Pradesh (12.1% vs. 8.9%). States such as Chandigarh, Delhi, Puducherry, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala, which have a higher proportion of literate and educated women, demonstrated better cognitive function outcomes. Approximately half of the women aged 45-59 in Mizoram (52%) and one-third in Himachal Pradesh (32%) reported reproductive health problems, with over 20% reporting such problems in Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Punjab. In contrast, older women in Tamil Nadu (10%), Andhra Pradesh (4%), Telangana (6%), and Goa (9%) reported lower prevalence rates of reproductive health problems.
In more than half of the states, the percentage of older women reporting mobility restrictions ranged broadly from 70% to 80%, compared to 50% to 65% among older men. Similarly, older women reporting functional limitations in activities of daily living (IADL) ranged from 50% to 65%, while for older men, it was between 35% and 50%.
These results confirm: a) higher rates of chronic health conditions and lower functional health outcomes among older women than men in most states; b) a higher prevalence of chronic health conditions in states advanced in demographic transition; and c) the geographic patterns of gender-based differences in education likely contribute to the observed disparities in both physical and mental health conditions between older women and men16. This pattern aligns well with well-established literature on gender-based inequalities in socioeconomic and health indicators across Indian states13,19. For instance, states with relatively high Human Development Indicators and stronger healthcare systems, such as Goa, Kerala, Chandigarh, and Puducherry, reported higher rates of diagnosis, treatment, and control of chronic health conditions for both older women and men4. In contrast, Nagaland and Lakshadweep, which have low literacy rates and limited access to healthcare services, showed lower treatment and control rates.
Disease burden shifting to older women: key policy messages
The burden of chronic health conditions and its impact on wellbeing among older women have remain understudied and under-recognized. Evidence-based policy making is crucial for planning health promotion and health care services of older women. Several conclusions including policy messages emerge from the evidence presented here. First, the results of gender disparities reported in this commentary are consistent with the recent overview of Global Burden of Disease study that reported excess disease burden of females than males, spanning age ranges from adolescence to older ages, at the global level and across seven world regions, from 1990 to 20212,3,11,13. Currently, NCDs, particularly cardiovascular diseases, cancers, respiratory diseases, diabetes, dementia, depression and musculoskeletal disorders – account for the greatest burden of death and disability among women11.
Second, females differ from males in many biological, social and economic factors that may fluctuate sometime but accumulate over time through life course, leading to different health experiences at each life stage and across regions3. From a comparative standpoint, men are more vulnerable to major life-threatening chronic diseases coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, emphysema, cirrhosis of the liver, and kidney disease, while women are more affected by chronic disorders, such as anaemia, thyroid conditions, migraine, arthritis, colitis, and eczema11,14. Non-life-threatening health conditions including osteoporosis, depression, and dementia and women’s specific conditions can significantly impact older women’s quality of life amplifying health disparities between older women and men. Additionally, lower early-life investments in human capital—such as nutrition and education for women compared to men—are known to contribute to female disadvantages in late-life health and well-being20. This also aligns with the cumulative disadvantage theory highlighting how early-life disadvantages impact health outcomes later in life – as life course trajectories are influenced by the accumulation of risks and available resources8,15.
Third, the adverse impact of health problems on India’s elderly women lives and wellbeing calls for an integrated healthcare and social support policies targeting older women in India. India’s older women deserve a comprehensive policy strategy that addresses healthcare, social factors and collaboration among policymakers, healthcare providers, and community organizations to achieve health policy goals for older women. The interaction between gender and the determinants and consequences of chronic diseases at older ages calls for different approaches to prevention, treatment and control13. Addressing the patriarchy driven structural and social determinants is an important policy pathway for the global region like India.
Fourth, the subnational pattern of gender disparities in ageing and health including gender specific diseases, symptoms and risk factors further highlight the need for both state and older women specific health and social care policy interventions13,15. The country’s subnational pattern of gender disparities in health and well-being mirror existing regional pattern of socioeconomic and health inequalities. India’s rapidly ageing demographics, particularly the rise in the number of elderly women including its regional demography, call for gender analysis to support policy development. Many serious health problems experienced by older women are often overlooked as a natural consequence of ageing and therefore, leading to under-reporting and delayed diagnosis despite their long-term physical and mental health consequences. Considering the widespread gender bias in India, the importance of spousal, family and community support must be recognized.
Lastly, there is a critical need for further research to understand and address the health challenges faced by India’s older women. Future studies should expand on chronic conditions in this population, including longitudinal research to explore gender differences in disease progression and the role of risk factors in chronic disease management. Additionally, conducting gender-specific subnational health outcome analyses, enhancing gender-sensitive data collection, raising awareness of chronic health conditions affecting older women, and incorporating intersectionality in health promotion are critical.

Responses