Uncovering the genetic architecture of inherited retinal disease in a consanguineous Iranian cohort

Introduction
Inherited retinal diseases (IRDs) are a group of genetic disorders that are caused by the dysfunction of photoreceptor cells and/or the underlying retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). With an incidence of one in 2000–3000 they affect more than two million people worldwide and are the most common cause of legal blindness in working-age adults in the UK and Australia1,2,3,4,5.
These blinding disorders display a large phenotypic heterogeneity, categorized in cone dystrophies (CDs), cone-rod dystrophies (CRDs), rod-cone dystrophies (RCDs) or generalized IRDs, mainly based on the predominant photoreceptors involved6. The clinical overlap between different IRDs complicates their diagnosis. Potential progression of the disease also varies depending on the IRD subtype. Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) for example, the most common IRD worldwide, is an RCD characterized by night blindness and a progressive loss of peripheral vision2. Additionally, specific IRD subtypes can be syndromic, affecting other systems besides the retina. A typical example is Usher syndrome, which combines IRD with sensorineural hearing loss6.
IRDs are also characterized by a remarkable genetic heterogeneity, which further contributes to their complexity. Currently, the Retinal Information Network (RetNet, https://retnet.org/) lists over 320 genes associated with IRD and novel disease genes are still being identified7,8,9,10. With approximately 5.5 million people affected, autosomal recessive (AR) inheritance is the most prevalent IRD inheritance pattern worldwide11. For RP specifically, AR inheritance occurs in 50–60% of cases, followed by autosomal dominant (AD) and X-linked (XL) in 30–40% and 5–15% of cases, respectively12.
It is estimated that nearly 40% of marriages in Iran are consanguineous, of which approximately 19% between first cousins13. As these unions result in autozygous identical-by-descent (IBD) regions inherited from a common ancestor, AR diseases occur more frequently13,14. Consequently, delineating IBD regions can aid the search for causal variants in consanguineous families. Performing autozygosity mapping, whereby runs of homozygosity (ROHs) are identified using genomic data, such as whole exome or genome sequencing (WES/WGS) is a powerful tool to pinpoint the potential regions in which causal variants occur in patients from consanguineous cohorts15. This advances a more comprehensive filtering and data analysis of exomic or genomic data.
Improving the diagnostic yield is critical for IRD patients, not only to confirm or re-visit the clinical diagnosis, often enabling a more accurate prognosis, but also to facilitate family planning and (future) therapeutic options. Despite the decreased cost and increased availability of next-generation sequencing methods such as WES and WGS, the genetic diagnosis of an estimated one third of IRD patients remains elusive16. A recent meta-analysis of studies published between 2018 and 2022 reports a diagnostic yield of 64.2%17. The specific combination of WES with autozygosity mapping results in diagnostic yields ranging from 68.4% to 100%18,19,20. In this study, we aim to elucidate the genetic diagnoses in IRD patients from a predominant consanguineous Iranian cohort, an understudied population, using an integrated autozygome-guided WES approach.
Results
The Iranian IRD cohort under study consisted of 192 index patients and 622 family members (Fig. 1a, Supplementary Data 1). Consanguinity was reported for 76.1% of the cohort, with the majority corresponding to first cousin marriages (54.7%) (Fig. 1b). DNA from family members was available for 153/192 (79.7%) index cases. The gender balance was approximately equal, with 55.2% male and 44.8% female index patients (Fig. 1c). An overview of the phenotypes present in the cohort can be seen in Fig. 1d. The majority of index patients were diagnosed with RP (42.2%), followed by Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA, 17.7%) and CRD (12.5%). Syndromic IRDs were reported in 9.9% of the cohort. Phenotypic evaluation, if the participants cooperated, included color fundus photograph, infrared (IR) imaging, fundus autofluorescence (FAF), fluorescein angiography (FA), optical coherence tomography (OCT), visual field (VF), and electroretinography (ERG). This was complemented with demographic findings and pedigree information. The clinical results are accessible through the Iranian National Registry of Inherited Retinal Diseases (IRDReg®) software.
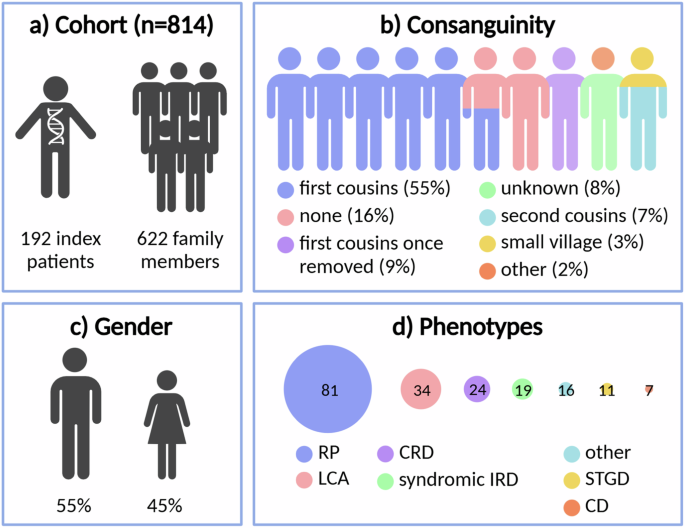
a Number of index patients and family members, b reported consanguinity, c gender, and d clinical phenotypes of the cohort. RP retinitis pigmentosa, LCA Leber congenital amaurosis, CRD cone-rod dystrophy, IRD inherited retinal disease, STGD Stargardt disease, CD cone dystrophy, other: all phenotypes not included in the remaining categories. Created in https://BioRender.com.
Autozygosity-driven WES-based testing elucidates the molecular cause of IRD in 72.9%
WES and subsequent analysis of single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) and copy number variants (CNVs) in a panel of known IRD-associated genes (RetNet panel) uncovered the (likely) cause of IRD in 140/192 (72.9%) index patients (Fig. 2a). These included 132 (68.7%) solved (one heterozygous class 4/5 variant for AD disease, one hemizygous class 4/5 variants for XL disease, one homozygous or two heterozygous class 4/5 variants in trans for AR disease) and 8 (4.2%) likely solved cases (two heterozygous class 4/5 variants without segregation data or a heterozygous class 3 variant in trans with a heterozygous class 4/5 variant for AR disease). Another 29 patients (15.1%) were considered to have an uncertain diagnosis, based on the presence of variants of uncertain significance (VUS) (class 3 variants for AD or XL disease, two heterozygous class 3 variants in trans, a heterozygous class 4/5 variant together with a heterozygous class 3 variant without segregation data, two heterozygous class 3 variants without segregation data or a homozygous class 3 variant for AR disease). No plausible cause of IRD was found for the remaining 23 patients (12.0%). The highest (likely) solved diagnostic yields were found in patients with ‘other’ (87.5%), Stargardt disease (81.8%) and LCA phenotypes (79.4%) (Supplementary Fig. 1). These are followed by CRD (79.2%), syndromic IRD (73.7%), RP (65.4%) and CD (57.1%). ‘Other’ phenotypes are those different from the mentioned categories and include patients with the following diagnoses: achromatopsia (n = 4), choroideremia (n = 4), bestrophinopathy (n = 3), Usher syndrome (n = 2), clumped pigmentary retinal degeneration (n = 1), early RCD with macular dystrophy (n = 1), Goldmann-Favre syndrome (n = 1), optic atrophy (n = 1) and retinitis pigmentosa or cone-rod dystrophy (n = 1).
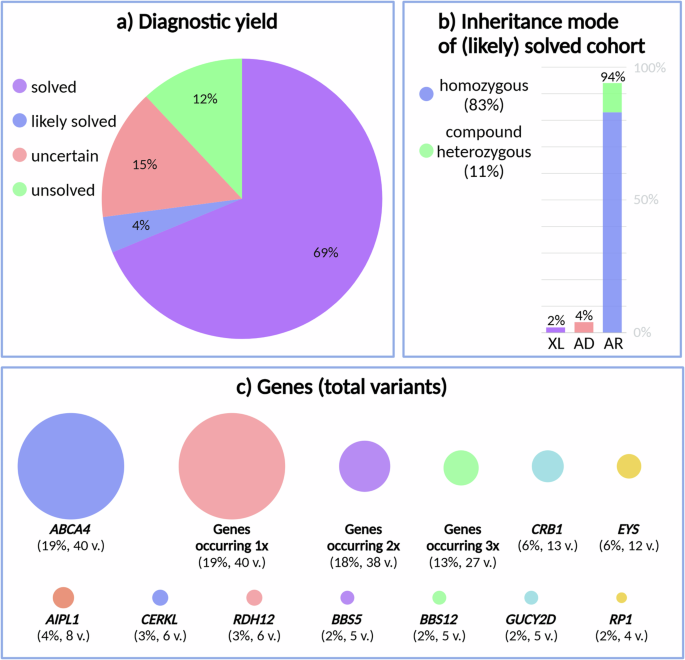
a Diagnostic yield, b identified inheritance mode in the (likely) solved cohort, and c genes in which variants were found (total number of variants: every occurrence counted once). XL X-linked, AD autosomal dominant, AR autosomal recessive, and v. variants. Created in https://BioRender.com.
Within the patient cohort that was considered to be (likely) solved or has an uncertain molecular diagnosis, the majority showed homozygosity for the identified variants (68.4%), followed by compound heterozygosity (23.4%), heterozygosity (6.2%) and hemizygosity (1.9%). For the (likely) solved patients only, AR inheritance was identified in 94.0%, with 82.8% corresponding to homozygous variants and 11.2% to compound heterozygous variants (Fig. 2b). Only 4.5% of (likely) solved patients were found to harbor variants in IRD genes associated with AD inheritance. Finally, variants in genes associated with XL inheritance were identified in 1.5% of the (likely) solved patients. Approximately 82.8% of variants found in patients with a known consanguineous background were located in an ROH.
The vast majority of identified variants in the IRD cohort are unique and novel
A total of 209 variants were identified across the solved, likely solved and uncertain cohorts, encompassing 78 distinct genes associated with IRD (Fig. 2c). Strikingly, the majority of these variants were unique (Fig. 3a). Among the cohort studied, the most frequently observed variant was c.5882 G > A, p.(Gly1961Glu) in the ABCA4 gene, occurring 7 times. Additionally, a CERKL variant (c.769 C > T, p.(Arg257Ter)) was found three times, followed by 14 other recurring variants, each appearing twice. For the (likely) solved IRD patients, 54.9% of variants were classified as pathogenic, 41.9% as likely pathogenic and 3.2% as VUS.
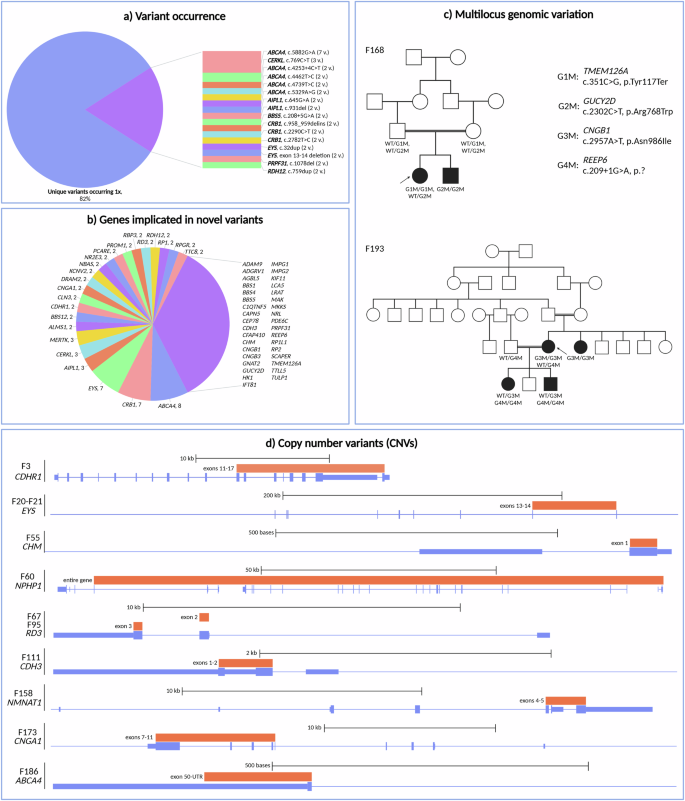
a Variant occurrence, b genes in which novel variants were found and the number of novel variants per gene (genes in which only one novel variant was found are grouped together at the right), c pedigrees of two families in which multilocus genomic variation was identified and d overview of the locations of the CNVs that were found in the cohort. WT wild type. Created in https://BioRender.com.
Out of the 187 unique variants, approximately half (52.9%) were novel. These novel variants were found in 58 distinct genes, with the largest number found in ABCA4 (n = 8; representing 26.7% of all ABCA4 variants), CRB1 (n = 7; 70.0% of CRB1 variants), EYS (n = 7; 70.0% of EYS variants), AIPL1 (n = 3; 50.0% of AIPL1 variants), CERKL (n = 3; 60.0% of CERKL variants) and MERTK (n = 3; 100.0% of MERTK variants). The other implicated genes are shown in Fig. 3b. The vast majority of novel SNVs (92.5%) were not present in the Iranome database, containing 800 Iranian healthy individuals from eight ethnic groups21. Only 7.5% could be found in Iranome, with a maximum frequency of five heterozygotes. Genes in which only novel variants were discovered and the number of variants are listed in Supplementary Fig. 2. Out of the 14 variants recurring twice (see above), six variants were novel and occurred in two patients each (AIPL1 c.931del, p.(Arg311Alafs*17); BBS5 c.208+5 G > A, p.?; CRB1 c.958_959delinsACATGTGAG, p.(Val320Thrfs*4); CRB1 c.2782 T > C, p.(Cys928Arg); PRPF31 c.1078del, p.(Arg360AlafsTer3) and RDH12 c.759dup, p.(Phe254LeufsTer19)).
Distribution of SNVs and CNVs in IRD genes shows 95% of SNVs and 5% of CNVs
The vast majority of the 187 identified variants (94.7%) in known IRD genes were SNVs: 43.9% missense variants, followed by 18.7% frameshift, 16.6% nonsense, 12.3% splice, 1.6% in-frame and 1.6% synonymous variants. A distribution of the most frequent genes in which SNVs were found, can be seen in Fig. 2c. Following SNV analysis, WES data from all patients was examined with ExomeDepth to identify potential CNVs. CNVs within known IRD genes were detected in 11/192 patients (5.3%) (Table 1). Notably, all CNVs were deletions (100.0%), identified in nine different IRD genes. Among these, an identical deletion in EYS was observed in two families, while two distinct deletions in RD3 were found in two different families. Most of the deletions were out-of-frame (80.0%). Single-exon deletions were identified in 40.0%, multiple-exon deletions in 50.0%, and a complete gene deletion in 10.0%. Additionally, 7/10 unique deletions (70.0%) were novel and located within the ABCA4, CDH3, CDHR1, CHM, CNGA1 and RD3 genes. The CNV positions relative to the genes are shown in Fig. 3d.
WES dissects distinct phenotypes resulting from multilocus genomic variation
In two families, more than one genotype segregated with disease, illustrating multilocus genomic variation. The pedigrees are shown in Fig. 3c. In F168, a homozygous TMEM126A variant (c.351 C > G, p.(Tyr117Ter)) (class 4) was identified in the index case. Segregation analysis revealed heterozygosity of this variant in both parents, but absence in an affected sibling. Further analysis of the affected sibling uncovered a homozygous GUCY2D variant (c.2302 C > T, p.(Arg768Trp)) (class 5), found in a heterozygous state in the index case and in both parents. The index case displayed optic atrophy, while the affected sibling was diagnosed with LCA, a distinct phenotype.
Another example of multilocus genomic variation was observed in F193, a family with RP. A homozygous CNGB1 variant (c.2957 A > T, p.(Asn986Ile)) (class 4) was found in the index patient and her affected sibling. The affected children of the index case were only heterozygous carriers, however. Upon further investigation, a homozygous REEP6 variant (c.209+1 G > A, p.?) (class 4) was identified in both affected children, with both parents being heterozygous carrier of this REEP6 variant.
Rare genotype-phenotype correlations
Two heterozygous NBAS variants (c.1194_1195del, p.(Asp398GlufsTer29) and c.5671 G > A, p.(Asp1891Asn)) were identified in the index patient of F34, diagnosed with LCA with no syndromic features. Available clinical data is presented in Supplementary Fig. 4. NBAS variants are associated with infantile liver failure syndrome (OMIM #616483) and short stature, optic nerve atrophy and Pelger-Huët anomaly (OMIM #614800). Additionally, one patient with NBAS variants has been described, presenting with CD, optic atrophy and Pelger-Huët anomaly but no other symptoms22. To our knowledge, no other non-syndromic cases have been previously reported in literature.
Two RP patients in the cohort were found to carry possible disease-causing DRAM2 variants (c.132-6 T > C, p.? and c.314 G > T, p.(Gly105Val)). The clinical diagnosis of one patient (F8) was refined to RP sine pigmento with macular involvement. The macular aspect of this phenotype could be in line with the DRAM2-associated AR retinal dystrophy with early macular involvement23. However, the phenotype of F97, end-stage RP without mention of macular problems, is atypical for DRAM2-associated IRD (see Supplementary Figs. 3 and 6 for available clinical data).
A homozygous CDH3 deletion of exons 1–2 was identified in F111, a patient with early RCD with macular dystrophy. CDH3 variants, however, are associated with congenital hypotrichosis with juvenile macular dystrophy (HJMD) (OMIM #601553)24. Symptoms of this disease are childhood-onset and progressive macular dystrophy combined with sparse scalp hair (hypotrichosis). Interestingly, CDH3 variants have also been shown to cause CRD, with the hypotrichosis confined to hypoplastic nails only25. In a family of Druze origin, three siblings with a CDH3 variant were additionally identified, their phenotype was described as RP, without skin or hair abnormalities26. Our findings could confirm this rare association of biallelic CDH3 variants with non-syndromic RP. Clinical reexamination to exclude extra-ocular symptoms was, however, not possible. Available clinical data is included in Supplementary Fig. 7.
Biallelic variants in CEP78 are typically associated with AR CRD and hearing loss (CRDHL) (OMIM #617236). Two causal variants (c.356 C > T, p.(Ser119Leu) and c.515 T > G, p.(Ile172Arg)) in this gene were found in homozygous state in two families in this Iranian cohort. In F141, with a clinical diagnosis of CRDHL (see Supplementary Fig. 8), c.515 T > G, p.(Ile172Arg) was identified, which has already been found in patients with CRDHL27. In F40, however, where the novel CEP78 variant c.356 C > T, p.(Ser119Leu) was identified, the phenotype was determined as RP without reported hearing impairment (see Supplementary Fig. 5). Other rare CEP78 cases have been described in literature: two siblings with non-syndromic RP28 and a patient with CRD without hearing loss29.
Phenotypic heterogeneity in genes associated with syndromic IRD
CLN3 variants can cause neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, a syndromic IRD (OMIM #204200), as well as isolated retinal dystrophy30,31,32,33. Both phenotypic presentations were also found in the studied cohort: syndromic IRD in F45 (c.1274_1275del, p.(Leu401ProfsTer7)) and isolated RP in F48 and F70 (c.1213 C > T, p.(Arg405Trp) and c.1056 G > A, p.(Gln352 = )). The variant in F48 has been described as a cause of non-syndromic retinal dystrophy in literature30,31,34,35. However, two siblings homozygous for this c.1213 C > T, p.(Arg405Trp) variant, initially diagnosed with isolated retinal dystrophy, developed neuronal symptoms in their third decade36. This variant is also homozygously present in F48, therefore monitoring of any late-onset neuronal symptoms will be advised. The other two identified CLN3 variants (c.1056 G > A, p.(Gln352 = ) and c.1274_1275del, p.(Leu401ProfsTer7)) have not yet been reported.
Discussion
The goal of this study was to elucidate the cause of IRD in a consanguineous cohort of 192 Iranian patients, and to characterize the genetic architecture of IRD in this understudied population. The Iranian population has been underrepresented in large-scale genomic databases such as gnomAD and the 1000 genomes project. As a countereffort, the Iranome database was established, containing data from 800 healthy individuals from the eight major ethnic groups present in Iran21.
To our knowledge, this was the largest NGS-based analysis of IRD in Iranian patients to date. Sabbaghi et al. described the creation of an Iranian retinal disease registry, where genetic testing of 122 families led to a diagnostic yield of 72%37, which is very similar to our diagnostic yield of 72.9%. Smaller scaled investigations in the Iranian population (ranging from 4 to 52 patients) generated diagnostic rates of 28%-100%19,20,27,38,39,40,41. Darbari et al., however, only examined 6 ABCA4 exons with Sanger sequencing in 18 Iranian Stargardt patients, explaining the low diagnostic yield of 28%41. Most other studies used WES27,39,40, or WES in combination with autozygosity mapping, similar to our approach, resulting in a molecular diagnosis of 90%19 and 100%20 of the examined cohort19,20. These high percentages can likely be explained by the significantly smaller cohort sizes of 10 and 17 families, respectively. WES, whether combined or not with autozygosity mapping, has been applied to other consanguineous populations as well, resulting in varying diagnostic rates in the Israeli/Palestinian (49%)26, Pakistani (62%)42, Tunisian (68%)18 and Saudi (73%)43 populations. Comparable diagnostic yields have been noted in non-consanguineous cohorts by targeted sequencing, WES, WGS or a combination thereof, ranging from about 41% to 76%44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52.
Approximately 76.1% of the cohort reported consanguinity, of which 54.7% corresponded to first cousins. The use of autozygosity mapping was especially beneficial in case of reported consanguinity, facilitating identification of the disease-causing variant by narrowing down the initial searching space to ROHs. The combination of WES with autozygosity mapping resulted here in a diagnostic yield of 72.9%. Not surprisingly, AR inheritance was identified in the overwhelming majority of (likely) solved cases (94.0%), with 82.8% presenting homozygously and 11.2% compound heterozygously. In 82.8% of patients from a consanguineous background variants were found to be located in an ROH. Although autozygosity-guided WES is a powerful first-tier screen to identify causal IRD variants in consanguineous cohorts, care should be taken to not exclusively focus on homozygous variants in ROHs, as AR IRD due to compound heterozygosity was demonstrated in 12 index cases with a reported consanguineous background. AD and XL IRD were also identified, in respectively five and two consanguineous cases. These findings underscored the need to additionally search for variants located outside of ROHs in patients with a consanguineous background.
In total, 209 variants were identified of which most were found in ABCA4 (19.1%), CRB1 (6.2%) and EYS (5.7%). In comparison, the most prevalent IRD genes worldwide are ABCA4 (30%), USH2A (12%) and EYS (8%)11. Strikingly, USH2A is also mentioned as one of most prevalent genes in for example Spanish, Portuguese, Argentinian, Mexican, Korean and Chinese cohorts44,45,46,47,51,52. In the Iranian population however, USH2A variants seem to be depleted, as this gene only accounts for IRD in two families (1.0%). This paucity of USH2A variants is corroborated by the previously mentioned studies on the Iranian population, with only one family out of 82 (1.2%) carrying an USH2A variant19,20,38,39.
Focusing on the 187 unique variants identified, approximately 94.7% were SNVs. The remaining 5.3% were deletions (CNVs). Notably, more than half of all variants (52.9%) were novel, allowing us to greatly expand the molecular spectrum of IRD disease genes.
Rare genotype-phenotype correlations were discovered in some cases, highlighting the importance of population-level genetic analyses to uncover such rare associations. The phenotypic heterogeneity, typically associated with IRD, was also illustrated in our cohort. For example, both the syndromic and isolated phenotypic presentations known for CLN3 variants were identified in Iranian patients. In one case (F48), the c.1213 C > T, p.(Arg405Trp) variant, which was described to cause later onset neuronal symptoms only in a homozygous state36, was also present homozygously. Therefore, follow-up of any neuronal symptoms is strongly advised.
An interesting feature of consanguinity seen in the cohort were two examples of multilocus genomic variation. In one family (F168), two siblings were diagnosed with optic atrophy and LCA respectively, caused by homozygosity of either the TMEM126A or GUCY2D variant segregating in the family. Multilocus variation can also span different generations, as illustrated in F193, a family with two consanguineous loops. Here, all affected individuals were diagnosed with RP, caused by a homozygous CNGB1 variant in the index and a sibling, and by a homozygous REEP6 variant in the children of the index patient. It is important to be aware that consanguinity may lead to unexpected and complex inheritance of variants.
Using a WES-based approach, this study provided 72.9% of the cohort with a molecular diagnosis, and identified 99 (52.9%) novel variants, thereby greatly expanding the molecular spectrum of IRD in Iran. These results emphasize the power and need of autozygosity-guided WES as a first-tier genetic test in consanguineous IRD cohorts. A genetic diagnosis allows to calculate recurrence risks, to identify potentially affected family members and to orient genetic counseling and reproductive decisions. A definite molecular diagnosis can provide a clear or more accurate prognosis for the patients, (re-)direct the clinical diagnosis and lead to the potential identification and allow timely follow-up of extra-ocular symptoms, for example in the case of the homozygous CLN3 variant (F48) that has been linked to late-onset neuronal symptoms. Monitoring of the non-syndromic NBAS patient (F34) will also be advised, in case any (late-onset) extra-ocular symptoms do occur. Additionally, more insights into the genetic landscape of IRD in this understudied population can inform population-specific genetic testing. Moreover, establishing a causative genotype is essential to select eligible patients for current and upcoming gene therapies as exemplified by the identification of disease-causing variants in actionable genes in this Iranian cohort: RPE65 (Luxturna®), ABCA4-related retinopathy (clinicaltrials.gov NCT06467344), CNGA1 (NCT06291935), CYP4V2 (NCT05399069), MERTK (NCT01482195), PDE6B (NCT03328130), RPGR (NCT04671433, NCT04517149) and non-syndromic RP (NCT03326336)53.
In addition, the unsolved patients for whom no definite molecular diagnosis could be provided (12.0%) using SNV and/or CNV analysis of the RetNet gene panel form an interesting discovery cohort of novel candidate IRD genes. Examples of recently identified novel candidate genes facilitated by the consanguineous background of patients are SAMD7, UBAP1L and CEP1627,8,9. Future perspectives for these patients include searching for (likely) pathogenic homozygous variants in the ROHs of consanguineous patients or WGS to uncover potential hidden non-coding variation and complex structural variation54.
Methods
Cohort
The Iranian cohort investigated in this study consisted of 192 index patients and 622 family members. DNA from family members was available for 153/192 (79.7%) index cases. Consanguinity was reported for 76.1% of the cohort, with the majority corresponding to first cousin marriages (54.7%).
This study adhered to the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Ghent University Hospital in Belgium and Research Institute for Ophthalmology and Vision Science at Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences in Iran (IR.SBMU.ORC.REC.1396.15). Written informed consent was obtained from all individuals or their legal representatives prior to genetic testing. A standard salting out protocol for DNA extraction was used37.
Patients were recruited from the Iranian National Registry of Inherited Retinal Diseases (IRDReg®) and the DNA samples were provided through the Eye Diseases DNA Biobank of the Research Institute for Ophthalmology and Vision Science affiliated to Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. All study participants underwent visual acuity assessment and color vision testing. Retinal examination was performed through a dilated pupil using a + 78D lens by a retina specialist. Color fundus photographs were obtained using a digital stereoscopic camera (Visucam Pro NM, Carl Zeiss Meditec AG, Germany). Infrared imaging (IR), fundus autofluorescence (FAF), and fluorescein angiography (FA; Heidelberg Engineering GmbH, Heidelberg, Germany) were also performed. Measurement of the central macular thickness was conducted by spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT; Spectralis, Heidelberg Engineering, Heidelberg, Germany). Humphrey visual field (VF; Carl Zeiss Meditec Inc., Dublin, CA, USA) testing, and electroretinography (ERG; RETIport 21 system, version 7/03, Roland Consult, Brandenburg an der Havel, Germany) were also performed.
Whole exome sequencing (WES)
Per family, one affected individual, typically the index patient, was selected for WES. Library prep and sequencing were performed using the SureSelectXT Human All Exon V7 kit (Agilent,) and 150 bp paired-end sequencing (NovaSeq 6000, Illumina, CA, USA) respectively. The resulting reads were mapped against the human hg38 reference genome (NCBI, GRCh38) with BWA-MEM v0.7.1755. SNVs and small insertions and deletions (indels) were detected with the GATK HaplotypeCaller (https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/201178v3) and annotated with the Ensembl Variant Effect Predictor (version 95) and dbNSFP (v3.5a)/dbscSNV (v1.1) databases56.
Resulting SNVs and small indels were filtered using the in-house WES analysis tool Seqplorer (unpublished) for the in-house RetNet panel consisting of 276 genes (version 4, https://www.cmgg.be/assets/bestanden/genpanel-RetNet_v4.pdf) and/or 290 genes (version 5, https://www.cmgg.be/assets/bestanden/Genpanel-RETNET-v5.pdf). The following parameters were initially employed for filtering in Seqplorer: variant frequency of 1% or 2% (respectively for AD and XL or AR expected inheritance), a genotype quality score of 20, a minimal depth of 2 and a medium or high impact severity (as defined by VEP57 and Gemini58). These parameters were adapted if necessary to include low impact or more frequent variants in genes such as ABCA4 or USH2A. All filtered variants were then analyzed, with the prioritization of homozygous variants in case of consanguinity and/or predicted AR inheritance. However, compound heterozygous variants or potentially other inheritance modes in these patients were also considered.
Detection, confirmation and segregation of CNVs
CNV analysis was performed using ExomeDepth (v.1.1.12), an R package for CNV calling on WES data. ExomeDepth identifies putative deletions and/or duplications based on the ratio of observed over expected reads59. qPCR following standard protocols was used to confirm all CNVs of interest in the cohort, as well as to examine segregation if DNA from family members was available60. The primers that were used for qPCR are listed in Supplementary Data 2.
Autozygosity mapping
The online tool AutoMap (Autozygosity Mapper, https://automap.iob.ch/) was consulted to identify ROHs in the WES data of the Iranian cohort15. VCF (Variant Call Format) files of the index patients were used as input. The determination of ROHs was performed using the default parameters: DP = 8, binomial = 0.000001, percaltlow = 0.25, percalthigh = 0.75, window = 7, windowthres = 5, minsize = 1, minvar = 25, minperc = 88, maxgap = 10, extend = 1 and chrX = no. ROHs were used for the prioritization of filtered variants in consanguineous families (Supplementary Data 3).
Confirmation and segregation analysis of SNVs
Genetic material from family members was available for 153/192 (79.7%) index patients. Segregation of the most promising SNVs and indels was investigated by Sanger sequencing, using the BigDye Terminator Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems) and an ABI 3730xl DNA Analyzer (Applied Biosystems) or by targeted NGS (MiSeq, Illumina, CA, USA), as described61. The primers used for segregation analysis are available in Supplementary Data 4. If the NGS quality score of SNVs and indels was too low, the presence of the called variant was examined by Sanger sequencing.
Variant classification
SNVs and indels were classified with the in-house tool VCT2020.2 (VariantClassificatieTool) into a class ranging from 1 (benign) to 5 (pathogenic), based on ACMG/AMP guidelines62. Variant frequency as reported in gnomAD (v.2.1.1 and v.3.1.2, https://gnomad.broadinstitute.org/) and classifications of the variant in variant databases ClinVar (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/) and LOVD (https://www.lovd.nl/) were considered. Furthermore, computational data and predictions, functional data, segregation data and allelic data were used to classify the variant. Variants were reported as novel if no mention of the variant was found in the literature.
Categorization into solved/likely solved/uncertain/unsolved cohorts was as follows: solved patients were determined to have one heterozygous class 4/5 variant for AD disease, one hemizygous class 4/5 variant for XL disease, one homozygous class 4/5 variant for AR disease or two heterozygous class 4/5 variants in trans. Two heterozygous class 4/5 variants without segregation data or a heterozygous class 3 variant in trans with a heterozygous class 4/5 variant were classified as likely solved. Uncertain cases comprised one heterozygous class 3 variant for AD disease or one hemizygous class 3 variant for XL disease. Moreover, two heterozygous class 3 variants in trans, a heterozygous class 4/5 variant together with a heterozygous class 3 variant without segregation data, two heterozygous class 3 variants without segregation data or a homozygous class 3 variant for AR disease were all determined to be uncertain. All other cases were reported as unsolved.




Responses